What is Deferred Revenue and Why is it a Liability?

A percentage of the sale is charged to the customer tocover the tax obligation (see Figure 12.5). The sales tax rate varies by state and localmunicipalities but can range anywhere from 1.76% to almost 10% ofthe gross sales price. Some states do not have sales tax becausethey want to encourage consumer spending. Those businesses subjectto sales taxation hold the sales tax in the Sales Tax Payableaccount until payment is due to the governing body.
Accounts Payable

By treating it as a liability for accounting purposes, you can keep the books balanced. It’s also useful for investment purposes, as unearned revenue can often provide fresh insight into a company’s potential future revenue. Unearned revenue is a short-term liability for the seller as the goods or services promised against the payment received are yet to be delivered. In simple words, it is the advance payment received from a customer against a promise to deliver products or services in the future. Unearned revenue refers to income received from a customer for products or services that are yet to be delivered. Assume, for example, that for the current year $7,000 of interest will be accrued.
- The adjusting entry for unearned revenue will depend upon the original journal entry, whether it was recorded using the liability method or income method.
- Using our example, when the landscaping company receives its $200, it will debit its cash account in the amount of $200 and credit its unearned revenue account in the amount of $200.
- This money, while in your cash account, isn’t really ‘yours’ yet—it’s sitting there with a condition attached.
- Taxes payable refers to a liability createdwhen a company collects taxes on behalf of employees and customersor for tax obligations owed by the company, such as sales taxes orincome taxes.
- Sometimes you are paid for goods or services before you provide those services to your customer.
- At Bench, we work with you to ensure your financial reporting needs are met while keeping you IRS compliant.
How Current Liabilities Work
Those businesses subject to sales taxation hold the sales tax in the Sales Tax Payable account until payment is due to the governing body. Taxes payable refers to a liability created when a company collects taxes on behalf of employees and customers or for tax obligations owed by the company, such as sales taxes or income taxes. A future payment to a government agency is required for the amount collected. Some examples of taxes payable include sales tax and income taxes.
- Interest payable can also be a current liability if accrual of interest occurs during the operating period but has yet to be paid.
- In the current year the debtor will pay a total of $25,000—that is, $7,000 in interest and $18,000 for the current portion of the note payable.
- It’s recognized proportionally as revenue on the income statement as the product or service is delivered over time.
- The contract will dictate when payments are due and when deliverables are to be met.
- In some industries, the unearned revenue comprises a large portion of total current liabilities of the entity.
- Therefore, under accrual accounting, if customers pay for products or services in advance, you cannot record any revenue on your income statement.
Join our newsletter for the latest in SaaS
Therefore, the revenue must initially be recognized as a liability. Note that when the delivery of goods or services is complete, the revenue recognized previously as a liability is recorded as revenue (i.e., the unearned revenue is then earned). Accrued expenses are listed in the current liabilities section of the balance sheet because they represent short-term financial obligations. Companies typically will use their short-term assets or current assets such as cash to pay them. Unearned revenue can provide clues into future revenue, although investors should note the balance change could be due to a change in the business.
Is Deferred Revenue an Operating Liability?
This occurs when customers prepay for a product or service, resulting in the company holding the funds as a liability on their balance sheet until the goods or services are delivered or rendered. Unearned revenue is an essential concept in accounting, as it impacts the financial statements of businesses that deal with prepayments, subscriptions, or other advances from customers. Unearned revenue is recorded when a firm receives a cash advance from its customer in exchange for products and services that are to be provided in the future. Since current liabilities are part of the working capital, a current balance of unearned revenue reduces a company’s working capital.
Deferred revenue: Is it a liability & how to account for it?
However, each accounting period, you will transfer part of the unearned revenue account into the revenue account as you fulfill that part of the contract. Unearned revenue, sometimes called deferred revenue, is when you receive payment now for services that you will provide at some point in the future. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees these rules and regulations to ensure proper disclosure and accurate representation of a company’s financial situation. Deferred revenue is typically reported as a current liability on a company’s balance sheet because prepayment terms are typically for 12 months or less.
Unearned revenue in the cash accounting system
Regularly reviewing and adjusting for unearned revenue allows for better financial decision-making and reporting. In the world of accounting, unearned revenue requires adjustments and corrections to ensure accurate representation https://www.bookstime.com/what-is-the-accounting-equation of a company’s financial statements. This section will discuss necessary adjustments and handling overstatements and understatements. The business has not yet performed the service or sent the products paid for.
In terms of financial statements, how is unearned revenue distinguished from deferred revenue?
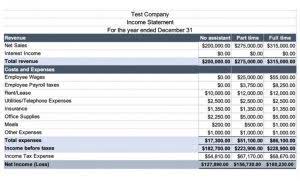
Deferred revenue is recorded as such because it’s money that hasn’t yet been earned. The payment is considered a liability to the company because there’s a possibility that the good is unearned revenue a current liability or service may not be delivered or the buyer might cancel the order. This is money paid to a business in advance, before it actually provides goods or services to a client.

Deferred Revenue and Accrual Accounting
